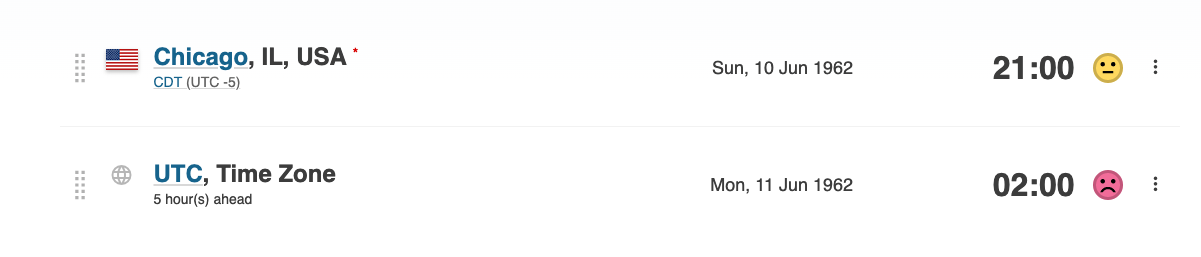
The Time Zone can be the reason.
The chart uses the UTC (Universal Time Coordinated) time zone to calculate the chart. We are caling Design Date (UTC).
Get the right UTC time to get the right Chart
Please use the Time Zone converter to check historical UTC time: https://www.timeanddate.com
Bodygraph Chart Time Zone API
The Time Zone Database (often called tz or zoneinfo) contains code and data that represent the history of local time for many representative locations around the globe. It is updated periodically to reflect changes made by political bodies to time zone boundaries, UTC offsets, and daylight-saving rules. Its management procedure is documented in BCP 175: Procedures for Maintaining the Time Zone Database.
https://www.iana.org/time-zones.
History if time zone in 1960’s
From 1945 to 1966, there was no federal law regarding Daylight Saving Time, so states and localities were free to choose whether or not to observe Daylight Saving Time and could choose when it began and ended. This understandably caused confusion, especially for the broadcasting industry, as well as for railways, airlines, and bus companies. Because of the different local customs and laws, radio and TV stations and the transportation companies had to publish new schedules every time a state or town began or ended Daylight Saving Time.
On January 4, 1974, President Nixon signed into law the Emergency Daylight Saving Time Energy Conservation Act of 1973. Then, beginning on January 6, 1974, implementing the Daylight Saving Time Energy Act, clocks were set ahead. On October 5, 1974, Congress amended the Act, and Standard Time returned on October 27, 1974. Daylight Saving Time resumed on February 23, 1975 and ended on October 26, 1975.
Inconsistent use in the U.S.
In the early 1960s, observance of Daylight Saving Time was quite inconsistent, with a hodgepodge of time observances, and no agreement about when to change clocks. The Interstate Commerce Commission, the nation’s timekeeper, was immobilized, and the matter remained deadlocked.
The Uniform Time Act
By 1966, some 100 million Americans were observing Daylight Saving Time based on their local laws and customs. Congress decided to step in and end the confusion, and to establish one pattern across the country. The Uniform Time Act of 1966 (15 U.S. Code Section 260a) [see law], signed into Public Law 89-387 on April 12, 1966, by President Lyndon Johnson, created Daylight Saving Time to begin on the last Sunday of April and to end on the last Sunday of October. Any State that wanted to be exempt from Daylight Saving Time could do so by passing a state law.
The Uniform Time Act of 1966 established a system of uniform (within each time zone) Daylight Saving Time throughout the U.S. and its possessions, exempting only those states in which the legislatures voted to keep the entire state on standard time.
Resources: